Stain wood pieces can enhance a home’s beauty and style. The right stain on furniture makes a huge difference when decorating a living space.
If you’ve never stained wood before or worked with a wood finish, don’t worry, we will show you. At the end, you will know how to turn your favorite bare wood furniture into small treasures.
History Of Wood Stain
In 1750, wax was used to stain wood. The practice carried over into the next century when woodworkers began using beeswax. During the Victorian Age, a wood surface was finished with hardening oil, varnish, and wax.
Oil-based stain, like walnut and linseed oil, rosin, amber, copal, gum, turpentine, and cheap wine were mixed so that it made wood harder and longer-lasting. The oil base would create a film over the surface to protect it from scratches, abrasions, and indoor moisture.
In the 1920s, stains were manufactured and became more available to the public.
In What Is The Difference Between Finish And Stain?
The difference between stain and finish is that the former adds color while wood finishes seal and protect wood from moisture. A stain isn’t a finish because it requires varnish or you have to apply a second coat of finish to protect the wood.
Also, finish is thicker than stain. Wood that has been stained and coated with polyurethane or lacquer will give the surface a richer color and a wet look. Remember, stains provide color, and not a finish.
Different Types Of Wood Grain Stain
Oil-Based Stains
Oil-based stain is the most popular worldwide for interior design projects. It is durable and can break through tough wood layers. Linseed oil is natural and non-toxic and preserves a wood finish or paint. Oil-based stains are versatile as they can be thinned with mineral spirits.
Water Based
Water-based stain is thinner because it uses water. It contains water-soluble aniline dyes that passes color. Water-soluble aniline dyes are chemically derived. The dyes are made with powder from coal.
These types of stains have strong pigments that bolster wood grains and leave surfaces with a smooth finish. One downside is they dry fast, which makes them hard to work with for DIY newcomers. With water-based stains, the most important step is cleaning and drying the wood’s surface.
Lacquer
As ironic as this may seem, lacquer stains don’t have lacquer in them, they’re just called lacquer stains. The stains dry fast and have an unmistakable odor due to the ketones and xylene in them. These types are thinner, which means they dry fast but require more than one coat.
Water-Soluble Dye
Water-soluble stains come in powder form. When mixing them, add an ounce of powder with one quart of water. For darker colors, increase the amount of powder in your mixture. They will fade after extended exposure to UV light, so it’s best if you use them on indoor furniture.
Metal Dye
Otherwise known as grain raising stains (NGRS), they are ready-to-use and dissolved in glycol ether blended with ethanol, retarder, or methanol. Unlike other stains, their color lasts longer and doesn’t fade easily.
Varnish Wood
These types are hard drying so they keep their color much better on wood surfaces. They are ideal for small wood projects. Although they are strong, you will need to apply more than one coat.
Gel
Gels are the newest addition to the stain family and were first made available to the public in the late 20th century. The stain is a high-viscosity liquid with thick, jelly pigments.
Can You Stain Green Treated Wood?
For outdoor wood projects, pressure-treated lumber is common. It is recommended to stain treated wood. Staining pressure-treated wood is good for outdoor wood furniture and structures. When working with treated wood, you can reduce surface cracking.
Types of Treated Wood
- Wet-treated wood – this is the most common and will be wet when you buy it. It may even “spit” at you when you nail it down. Let it dry before you stain it.
- Water repellent treated wood – look for a tag that says “Thompsonized” or ask the dealer if your lumber is this type.
- Kiln-dried pressure-treated lumber -stain the wood immediately with water based stains.
DIY Level: Beginner
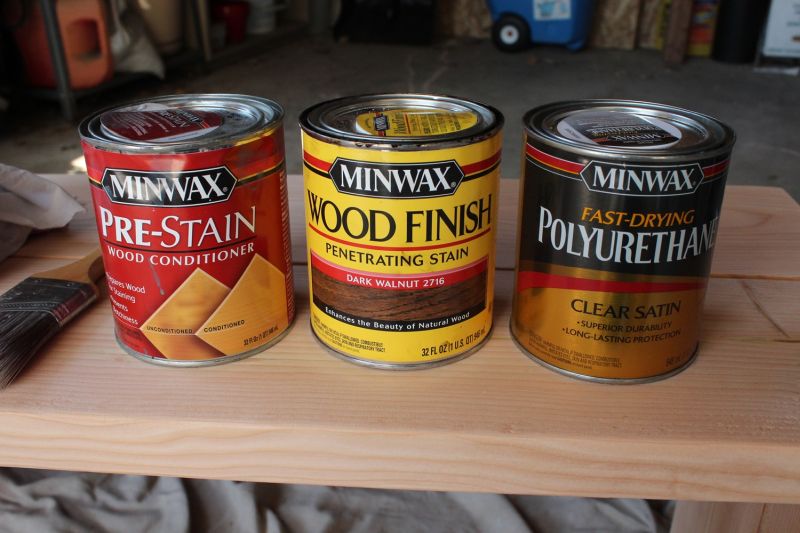
Stain Wood Materials:
- Unfinished or scrap piece of wood, clean and dry.
- Wood conditioner.
- Stain of your choice.
- Wood finishing coat, such as polyurethane.
- Bristle brush.
- Lint free rags.
- Drop cloth.
Note: The pre-stain, stain, and topcoat must be compatible. If one is oil-based, the others must be oil-based. A water-based stain doesn’t work well on top of oil-based pre-stains, for example.
Stain Wood – A Step By Step Guide
Start with pre-stain, or pre stain wood conditioner
Begin with your pre-stain, or pre stain wood conditioner. Make sure the piece is clean and dry. When you prep wood, there should be no finishes on it or this will not work. Use a stripping agent to remove previous finishes.
Pre Stain Wood Conditioner
Apply pre-stain wood conditioner with a clean bristle brush to a portion of your wood. If the pre-stain is absorbing, move to the rest of your wood piece.
Cover the wood with pre-stain wood conditioner so it evens the wood and the stain will be absorbed.
Allow Pre Stain Wood Conditioner To Dry
Wait 5-15 minutes for the pre-stain wood conditioner to be absorbed before you start staining.
Clean Surface
Use a lint free cloth to clean the surface.
Top Coat
You have a small window to apply the first coat for best results, about two hours. Stir the stain (remember, use oil-based if your pre-stain is oil-based), to avoid air bubbles. Stir during the entire process, depending on the size of the project.
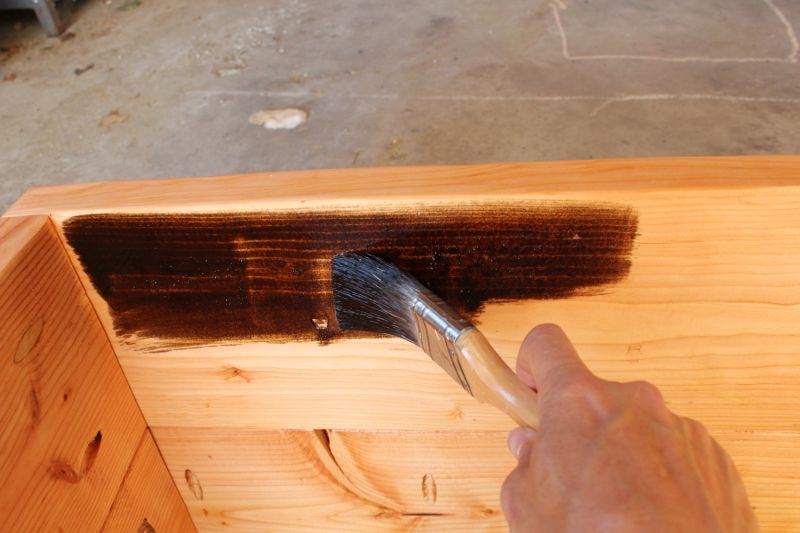
Apply Stain
Apply the stain to an inconspicuous spot with. a bristle brush, such as the underside of the bench.
Stain an inconspicuous spot on your piece, such as the underside of the bench.
Apply the stain in the direction of the wood grain. Be sure to brush away drips, as these may cause odd lines or unevenness in your finished stain. You can use a tack cloth to catch any waste.
Work in small sections, one area at a time, to create an even stain.
Allow Stain To Dry
Wait 5-15 minutes for the stain to absorb. (This example shows a 7-minute absorption time of Dark Walnut stain.) The longer the stain has to absorb into the wood, the deeper the color, the darker the wood will be.
Wipe Clean
Remove excess stain with a clean cloth. Don’t let the excess sit on your unfinished wood. It will look blotchy and will be sticky.
After staining the hidden areas, you’re ready to finish your wood project. Be sure to check the time and follow in the same manner so your stain will absorb evenly.
After applying, waiting, and wiping the stain over your wood piece, take a break. You’ll need to wait at least eight hours or more, depending on the humidity and temperature. Allow the stain to absorb and dry.
If for some reason you decide a few hours later that you want your wood piece a bit darker, reapply a second coat of stain, following the same procedure. Allow it to dry after the second coat of stain has been wiped away.
Protective Coat
After the stain has dried, and you like the result, apply the protective coat. Remember, the top coat should be the same as your pre-stain and stain – oil-based to oil-based, water-based to water-based. This example uses a clear coat polyurethane for the finishing coat.
Stir the polyurethane and mix the bottom of the can. Do not shake as this would cause air bubbles.
Use a natural bristle brush or foam brush to apply the polyurethane. When staining wood, you’ll want to apply it with the grain in an even but light coat. Allow the poly to dry for 3-4 hours or until it is dry and not tacky. Lightly sand with 220-grit sandpaper, wipe clean and apply a second coat.
Second Coat Of Stain
Repeat the sand-and-apply-poly process several times. This example shows two coats of polyurethane. Allow 48 hours for the polyurethane to dry.
Final Result
Congratulations. You’ve just completed your wood project.
It’s amazing how stained wood can make common wood look stunning.
How to Stain Wood Darker
Before you can make wood darker, make sure the existing stain is compatible with what is already on the wood.
Preparation
Remove excess parts from the wood that you want to stain. For example, if you’re working on a door, remove the doorknobs and handles.
Sanding Stain Wood
Use TSP soap or a degreasing sap to clean the wood surface before applying the new stain. Dust or grime will prevent it from sticking and could give the surface a bumpy look.
Sand the surface with medium grit sandpaper or 220 grit sandpaper for a textured feel. It will help the stain adhere to the surface.
Apply Wood Stain
Apply wood stain to the surface with a tack cloth or synthetic bristle brush. Use it evenly and go with the direction of the grain or in a circular motion. You could also try a lint free rag for smaller projects.
If staining over a polyurethane surface, use a gel stain. Polyurethane is a sealer that makes surfaces non-absorbent. A gel will complement the surface.
Toner
If you want a darker color, toner will help. Toners can remove unwanted yellow and green spots. A toner will also add to the project’s shelf-life as it provides extra surface protection. Allow the toner to dry for 24 hours. Before you reassemble the wood project, wipe it with a damp cloth.
How To Stain Wood Frequently Asked Questions
Why Does Some Stain Wood Not Take Stain?
Wood takes stain differently based on its surface and if it’s already sealed. Stain cannot sit on wood, but should soak and dry in wood pores. If the wood you’re working with has been sealed by polyurethane or a finish, it will be useless because it won’t reach the wood pores.
Can You Use Wood Conditioner After Staining?
Do not put a wood conditioner over wood stain. You should use wood conditioner beforehand. If you apply a conditioner afterward, it will remove the stain.
How Long Does Wood Stain Take To Dry?
On average, after applying stain, it will take between 24 and 48 hours to dry. Depending on your wood furniture, you might need to wait 72 hours before applying polyurethane to finish your project.
How To Get Wood Stain Off Skin?
You can remove wood stains with rubbing alcohol or isopropyl alcohol and acetone. Use a clean rag and solvents and rub the skin. Afterward, rinse your skin with lukewarm water and soap.
Can You Paint Over Stained Wood Without Priming?
If your paint adheres without bleed-through, you can paint over stained wood and you won’t have to prime. If streaks appear, then you will need to prime with a bonding, stain-blocking primer.
How To Get Wood Stain Out Of Carpet?
To remove wood stain from your carpet, you can use acetone and a lint free rag as a DIY solution. Blot the stain and wipe. For bigger stains, WD-40 or lacquer thinner will help break down the stain particles. If all else fails, enlist the services of a professional carpet cleaner and steam clean the carpet stains.
How To Stain Wood Conclusion
Staining wood is a great way to tap into your DIY skills. The only daunting thing about staining is that it’s permanent. And because there are multiple products available, it’s understandable if staining wood might be difficult if it’s your first time.
You need to know what you’re working with, from oil based and water-based stains to pre stain wood conditioner. Remember, wood stains provide color, not a finish.
After you’ve used stain and you have some leftover, do not throw it away. Stains are pricey, but they’ll be fine sitting in a can for extended periods. If a skin coat forms on the top, then throw it away.
The post How to Stain Wood: A Basic Step By Step Process appeared first on Home Decorating Trends - Homedit.






















0 Commentaires